D. Pair of Numbers
time limit per test
2 seconds
memory limit per test
256 megabytes
input
standard input
output
standard output
Simon has an array a1, a2, ..., an, consisting of n positive integers. Today Simon asked you to find a pair of integers l, r (1 ≤ l ≤ r ≤ n), such that the following conditions hold:
- there is integer j (l ≤ j ≤ r), such that all integers al, al + 1, ..., ar are divisible by aj;
- value r - l takes the maximum value among all pairs for which condition 1 is true;
Help Simon, find the required pair of numbers (l, r). If there are multiple required pairs find all of them.
Input
The first line contains integer n (1 ≤ n ≤ 3·105).
The second line contains n space-separated integers a1, a2, ..., an (1 ≤ ai ≤ 106).
Output
Print two integers in the first line — the number of required pairs and the maximum value of r - l. On the following line print all l values from optimal pairs in increasing order.
Sample test(s)
input
5 4 6 9 3 6
output
1 3 2
input
5 1 3 5 7 9
output
1 4 1
input
5 2 3 5 7 11
output
5 0 1 2 3 4 5
Note
In the first sample the pair of numbers is right, as numbers 6, 9, 3 are divisible by 3.
In the second sample all numbers are divisible by number 1.
In the third sample all numbers are prime, so conditions 1 and 2 are true only for pairs of numbers (1, 1), (2, 2), (3, 3), (4, 4), (5, 5).
A similar question to dominoes principle codeforces that uses the amortisation of o(n^2) dp to o(n).
Here we need just see an observation
k......l........m
if l divides any number before it suppose a[l] divides a[l-1] then it also divides all numbers that al divides.
Hence we can go backwar in steps like these j-=dp[j] and break when the jth element is not divisible by i.
as further segment is not possible
Now we do this in a forward fashion and backward fashion and generate the answer and the starting index.
Code
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
struct node
{
int f;
int b;
} dp[300010];
int a[300010];
int main()
{
int n;
cin>>n;
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++)
{
cin>>a[i];
}
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++)
{
dp[i].f=1;
dp[i].b=1;
}
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++)
{
// cout<<"i "<<i<<endl;
for(int j=i-1;j>=1;j-=dp[j].f)
{
// cout<<" j "<<j<<endl;
if(a[j]%a[i]!=0)
{
// cout<<"break for "<<j<<endl;
break;
}
// cout<<"added "<<j<<endl;
dp[i].f+=dp[j].f;
}
}
for(int i=n;i>=1;i--)
{
for(int j=i+1;j<=n;j+=dp[j].b)
{
if(a[j]%a[i]!=0)
break;
dp[i].b+=dp[j].b;
}
}
/*for(int i=1;i<=n;i++)
cout<<dp[i].f<<" ";
cout<<endl;
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++)
cout<<dp[i].b<<" ";
cout<<endl;*/
int ans=0;
int cnt=0;
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++)
{
int temp=dp[i].f+(dp[i].b)-1;
if(temp>=ans)
{
if(ans==temp)
cnt++;
else
{
cnt=1;
ans=temp;
}
}
}
set<int> res;
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++)
{
if(dp[i].f+(dp[i].b)-1==ans)
{
// cout<<"i "<<i<<endl;
res.insert(i-dp[i].f+1);
}
}
cout<<res.size()<<" "<<ans-1<<endl;
int l=res.size();
set<int>::iterator it;
for(it=res.begin();it!=res.end();it++)
{
cout<<*it<<" ";
}
return 0;
}

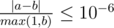 .
.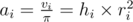
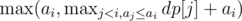
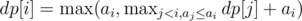 ? We use a max-segment tree which does these two operations:
? We use a max-segment tree which does these two operations: